Hip Treatments
Home >> Hip Treatments
Hip Joint Replacement
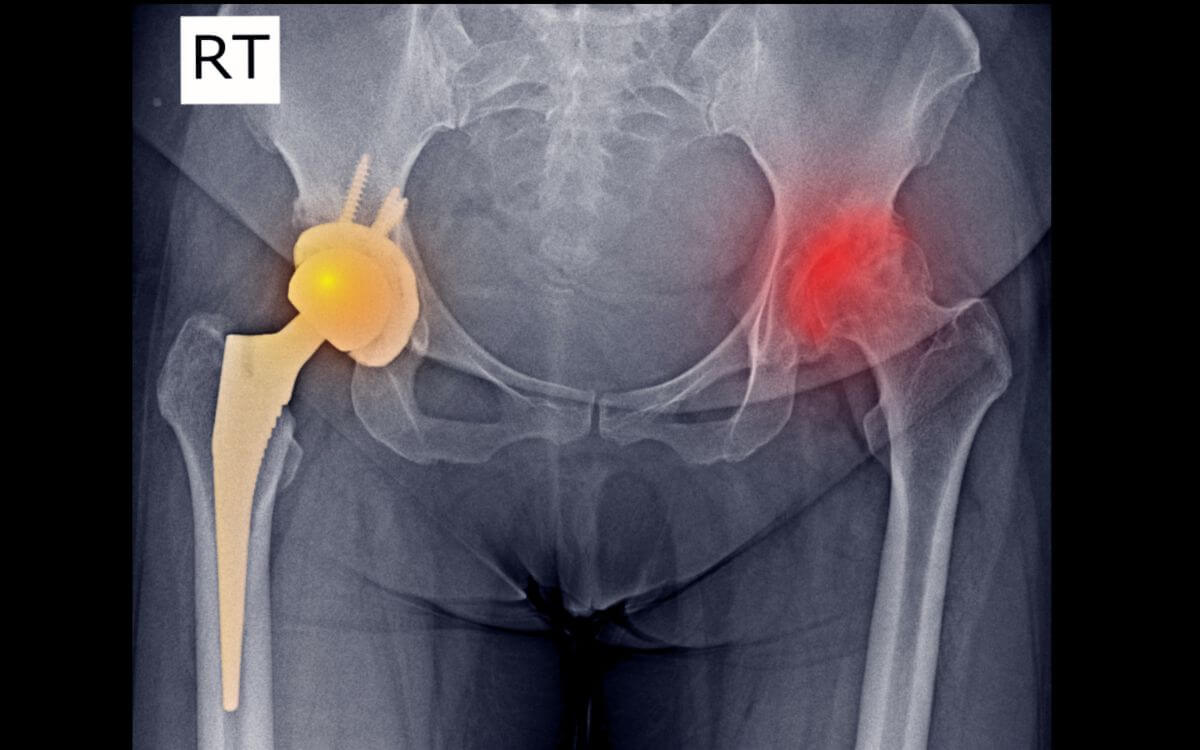
Hip Joint Replacement
The hip joint is essential for mobility, stability, and weight-bearing tasks in our everyday life. However, when the hip joint is harmed or degenerates as a result of several reasons, it may cause crippling pain and a marked decrease in quality of life. Hip joint replacement surgery becomes a game-changing option in these situations, providing pain relief, increased mobility, and a chance to reclaim independence.
Understanding Hip Joint Replacement:
Hip arthroplasty, sometimes referred to as hip replacement surgery, replaces the diseased or injured hip joint with artificial parts. The process entails removing the worn-down bone and cartilage from the hip joint and replacing them with prosthetic elements that closely resemble the native joint’s composition and functionality. Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, avascular necrosis, hip fractures, and deformities are among the disorders that are most often treated with hip replacement surgery.
Hip joint replacement advantages:
1. Pain relief: Hip joint discomfort may be terrible and have a significant influence on a person’s day-to-day activities. Surgery to replace the hip joint efficiently reduces pain, enabling patients to carry out daily tasks and exercise with a great deal less difficulty.
2. Restored mobility: A hip joint replacement restores the stability and functioning of the joint by replacing the worn-out joint surfaces. Individuals may now walk, climb stairs, and engage in other activities that were previously impossible or severely restricted by hip pain and dysfunction.
3. Better quality of life: Chronic hip pain may seriously reduce a person’s quality of life by interfering with their ability to work, sleep, and take part in leisure activities. Surgery to replace the hip joint reduces discomfort, improves mobility, and fosters independence, all of which boost general wellbeing and quality of life.
The replacement of the hip joint:
The following stages are involved in hip joint replacement surgery, which is normally carried out under general or local anaesthesia:
To reach the hip joint, an incision is made along the side or rear of the body.
Replacement of damaged bone and cartilage: The hip joint’s damaged bone and cartilage are carefully replaced.
Implant placement: Using specialised surgical methods, the artificial hip components—including the metal or ceramic femoral stem, ball, and socket—are placed into the hip bone.
Closure: A sterile dressing is used after the wound is stitched or stapled shut.
Rehabilitation and Recuperation:
For a complete recovery and the restoration of hip function, post-operative care and rehabilitation are essential. Physical therapy is often used in rehabilitation to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion. Cold treatment and other pain-management techniques are used to reduce post-operative discomfort. Under the supervision of medical personnel, patients will progressively enhance their weight-bearing activities. The time it takes to recuperate varies based on personal conditions, but most people may return to their regular activities in a few months.
Observations and Prognosis: Although hip replacement surgery has several advantages, the following points should be taken into account:
Implant longevity: Today’s hip implants are made to be strong and long-lasting. They could ultimately break down, particularly if there is too much stress or too much exercise. Patients should talk to their surgeon about the anticipated implant lifetime.
Pre-existing medical problems: Before having hip replacement surgery, it is essential to make the surgeon aware of any pre-existing medical disorders. Additional precautions or treatment techniques may be necessary for certain situations, such as an infection or uncontrolled diabetes.
Dedication to rehabilitation: For a satisfactory result, active engagement in post-operative rehabilitation, including physical therapy exercises and lifestyle changes, is essential. following the suggested recovery regimen
